The best passwords will thwart brute force and dictionary attacks, but it's also possible to make them easy to remember. Try these password ideas to make your accounts unbreakable.
Your passwords grant access into your own personal kingdom, so you are probably thinking 'what are the best practices to create a strong password' to protect your accounts against these cybercriminals. If your passwords were part of a breach, you will want to change them immediately.
The anatomy of a strong password
Now that we know how passwords are hacked, we can create strong passwords that outsmart each attack (though the way to outsmart a phishing scam is simply not to fall for it). Your password is on its way to being uncrackable if it follows these three basic rules.
Don’t be silly
Stay away from the obvious. Never use sequential numbers or letters, and for the love of all things cyber, do not use “password” as your password. Come up with unique passwords that do not include any personal info such as your name or date of birth. If you’re being specifically targeted for a password hack, the hacker will put everything they know about you in their guess attempts.

Can it be brute force attacked?
Make it long.
This is the most critical factor. Choose nothing shorter than 15 characters, more if possible.
Use a mix of characters.
The more you mix up letters (upper-case and lower-case), numbers, and symbols, the more potent your password is, and the harder it is for a brute force attack to crack it.
Avoid common substitutions.
Password crackers are hip to the usual substitutions. Whether you use DOORBELL or D00R8377, the brute force attacker will crack it with equal ease. These days, random character placement is much more effective than common leetspeak* substitutions. (*leetspeak definition: an informal language or code used on the Internet, in which standard letters are often replaced by numerals or special characters.)
Don’t use memorable keyboard paths.
Much like the advice above not to use sequential letters and numbers, do not use sequential keyboard paths either (like qwerty). These are among the first to be guessed.
Recommended ways to improve your password
All of the above methods help to strengthen your passwords but aren’t very workable, given that the average person uses dozens of them. Let’s review a few ways we recommend: use new complex passwords and a password manager, install an authenticator app on your smartphone, and purchase new hardware. Each of these can help with better and more secure authentications.
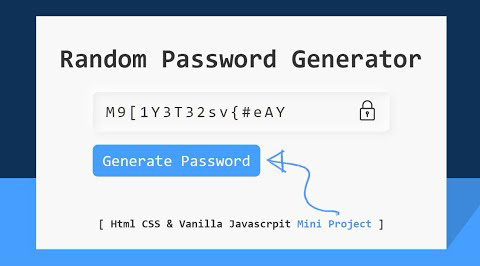
Use a password manager and a random password generator
A password manager keeps track of all of your passwords and does all the remembering for you, except for one thing — the master password which grants you access to your password manager. For that big kahuna, we encourage you to use every tip and trick listed above.The programs also come with generators, such as the Avast Random Password Generator shown below, so you can create super-complicated, extra-long passwords that are infinitely more difficult to crack than any passwords a human might come up with. PC Magazine has a series of recommendations of password managers here.
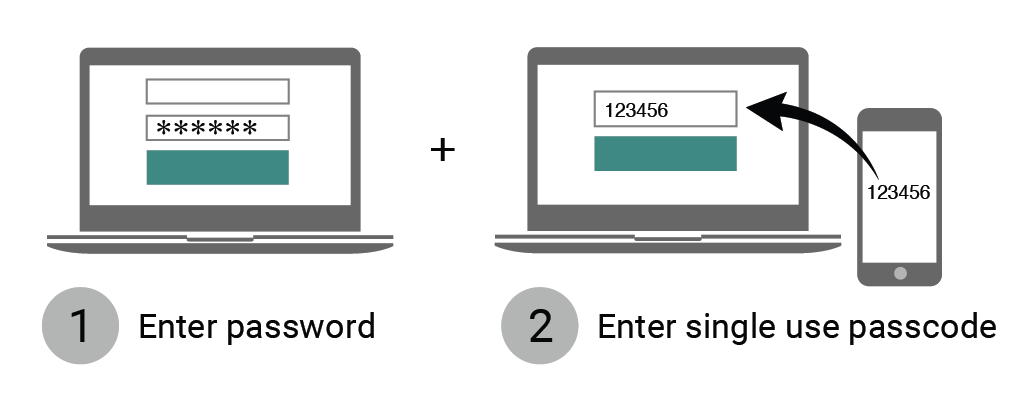
Use multi-factor authentication.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection (which becomes your first layer of protection should your account details ever get leaked). These have become the new industry standard for effective security. In our blog post here, we explain how they are used and how you can add MFA to common social accounts such as Twitter and Facebook. They require something in addition to a password, such as biometrics (fingerprint, eye scan, etc.), or a physical token. This way, as simple or complex as your password is, it’s only half of the puzzle.
Be careful who you trust
Security-conscious websites will hash its users’ passwords so that even if the data gets out, the actual passwords are encrypted. But other websites don’t bother with that step. Before starting up accounts, creating passwords, and entrusting a website with sensitive info, take a moment to assess the site. Does it have https in the address bar, ensuring a secure connection? Do you get the sense it is up on the newest security standards of the day? If not, think twice about sharing any personal data with it.

